How to use Cisco Security Reference Architecture
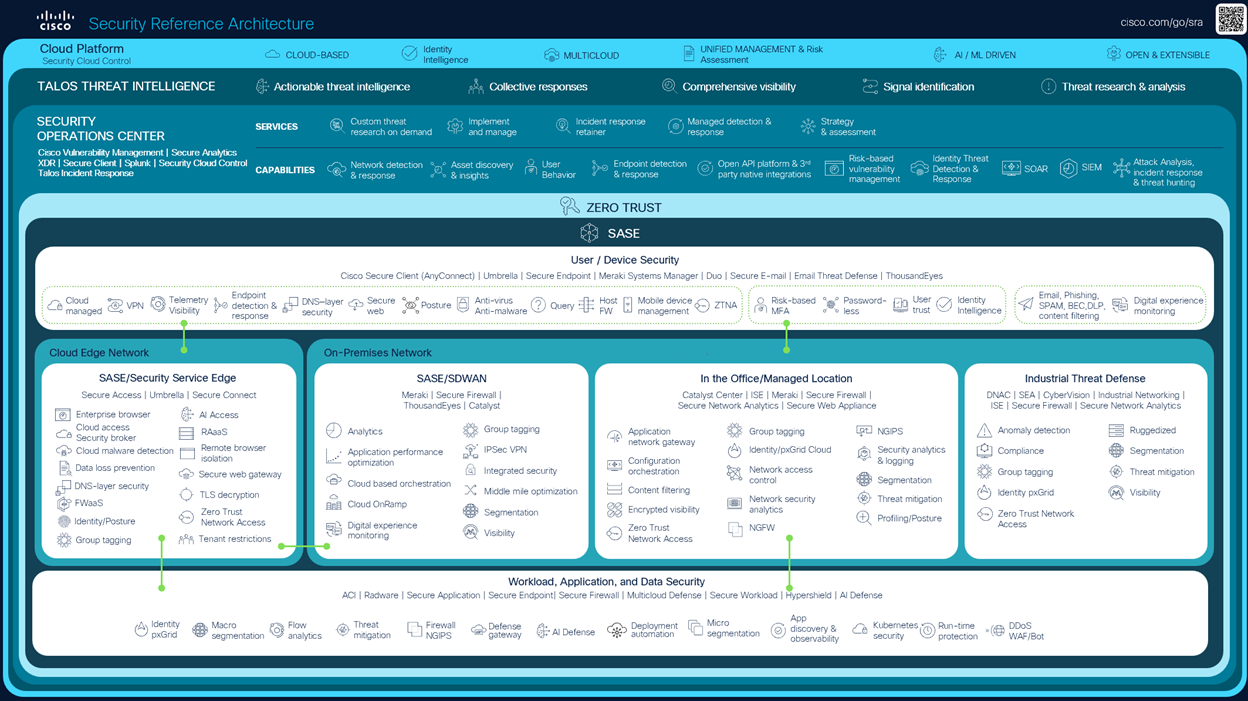
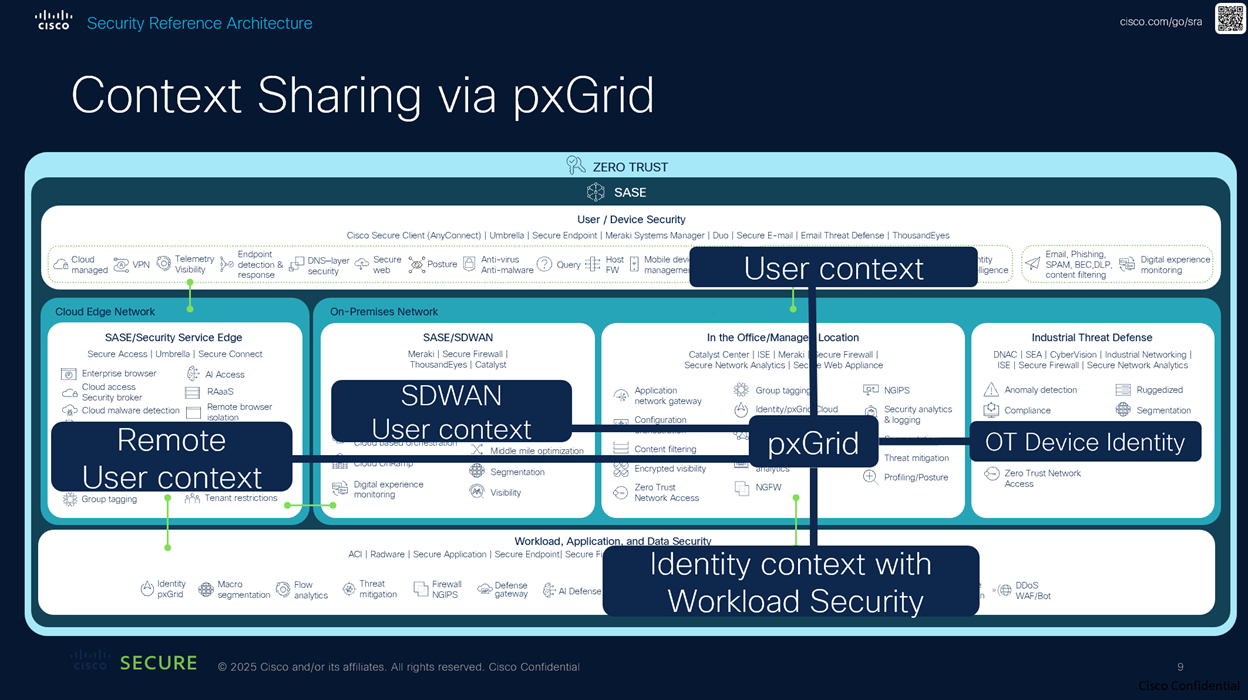
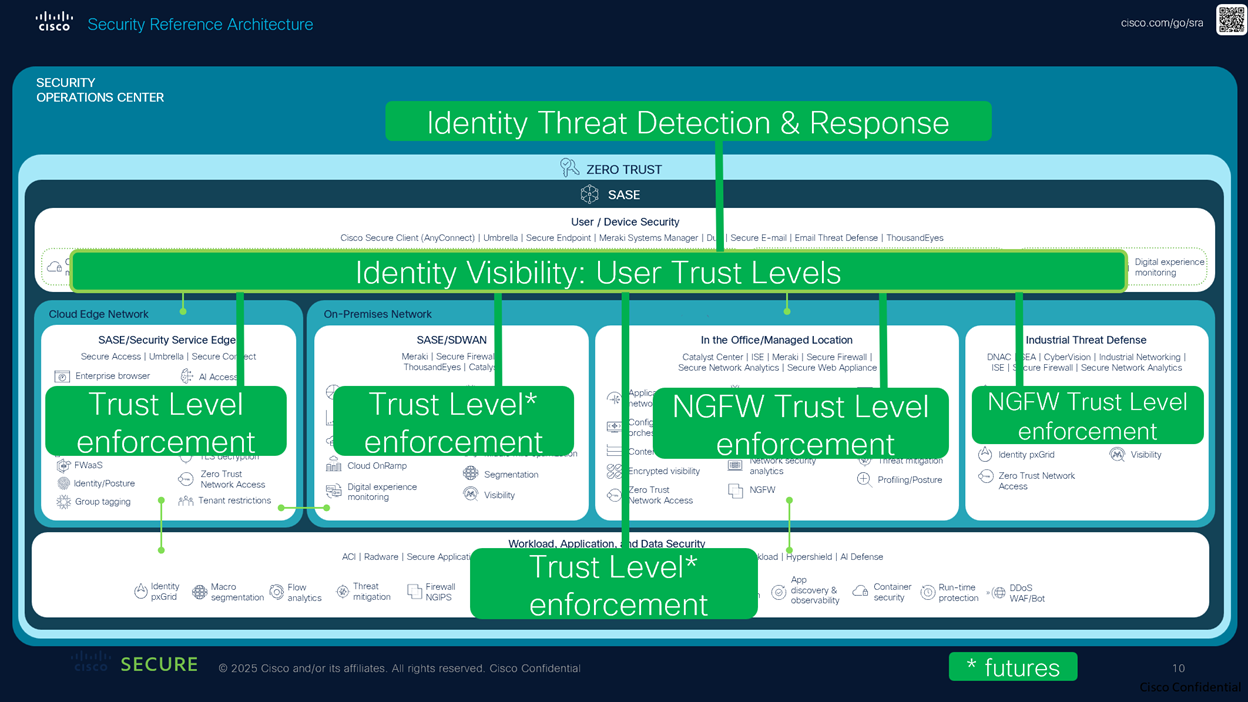
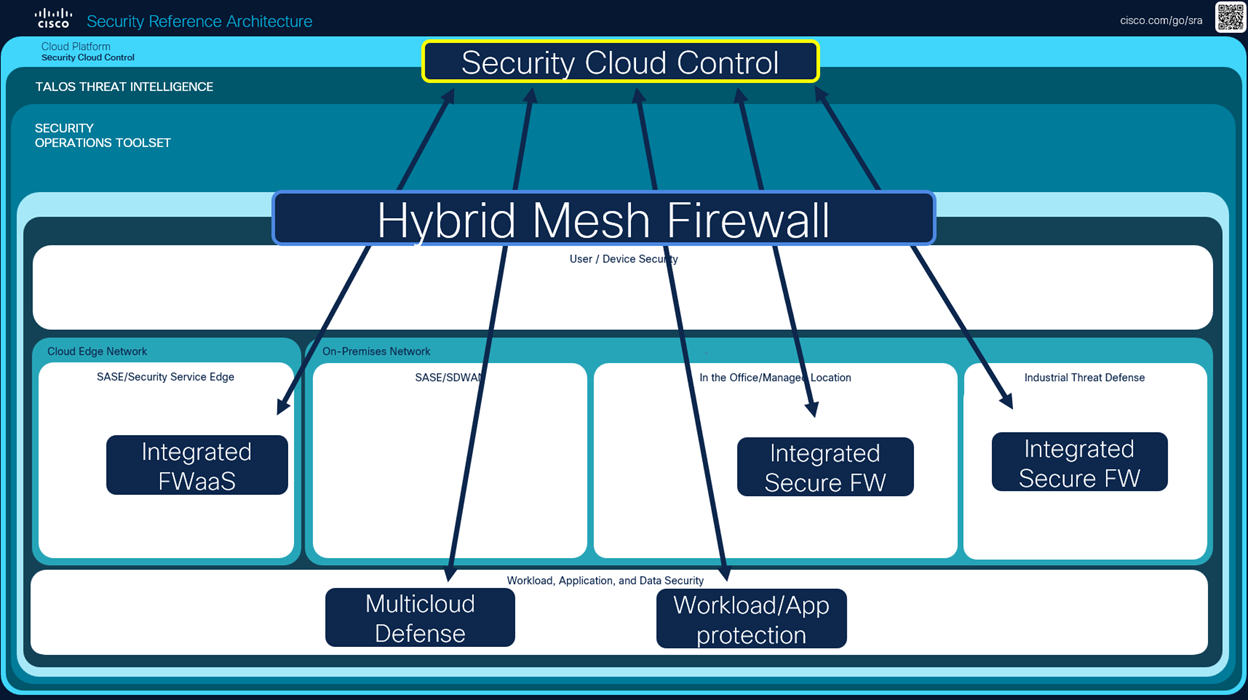
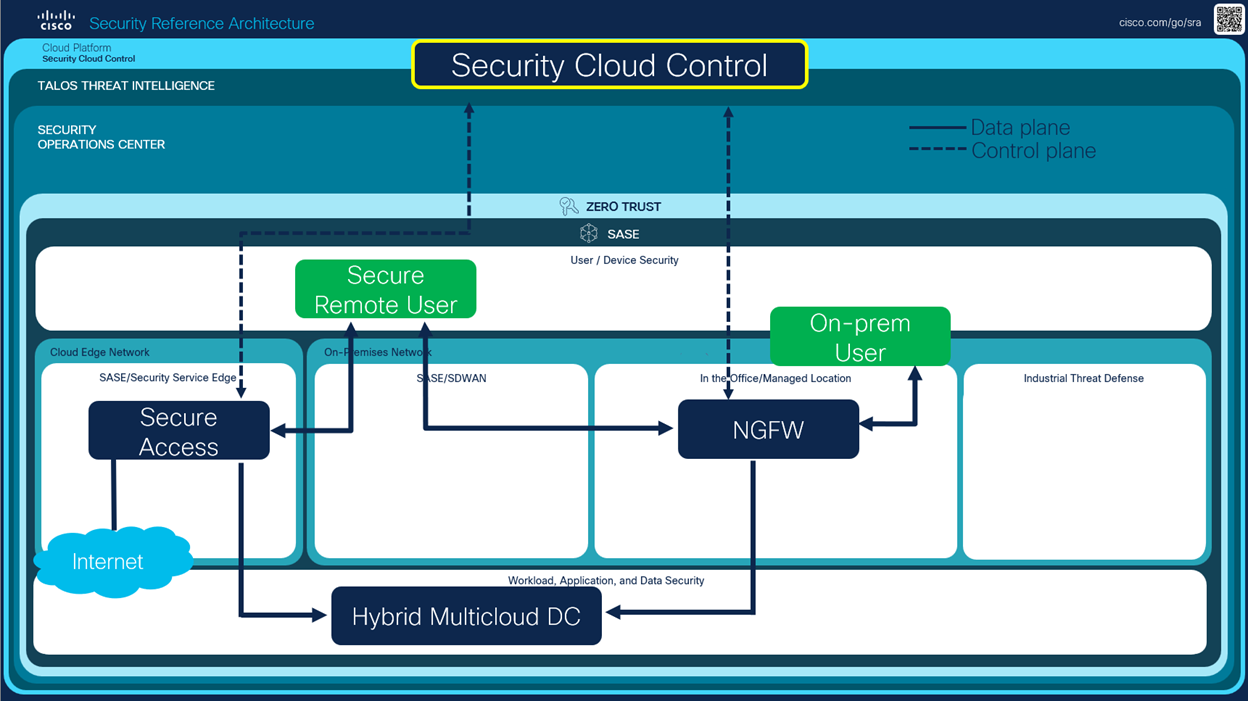
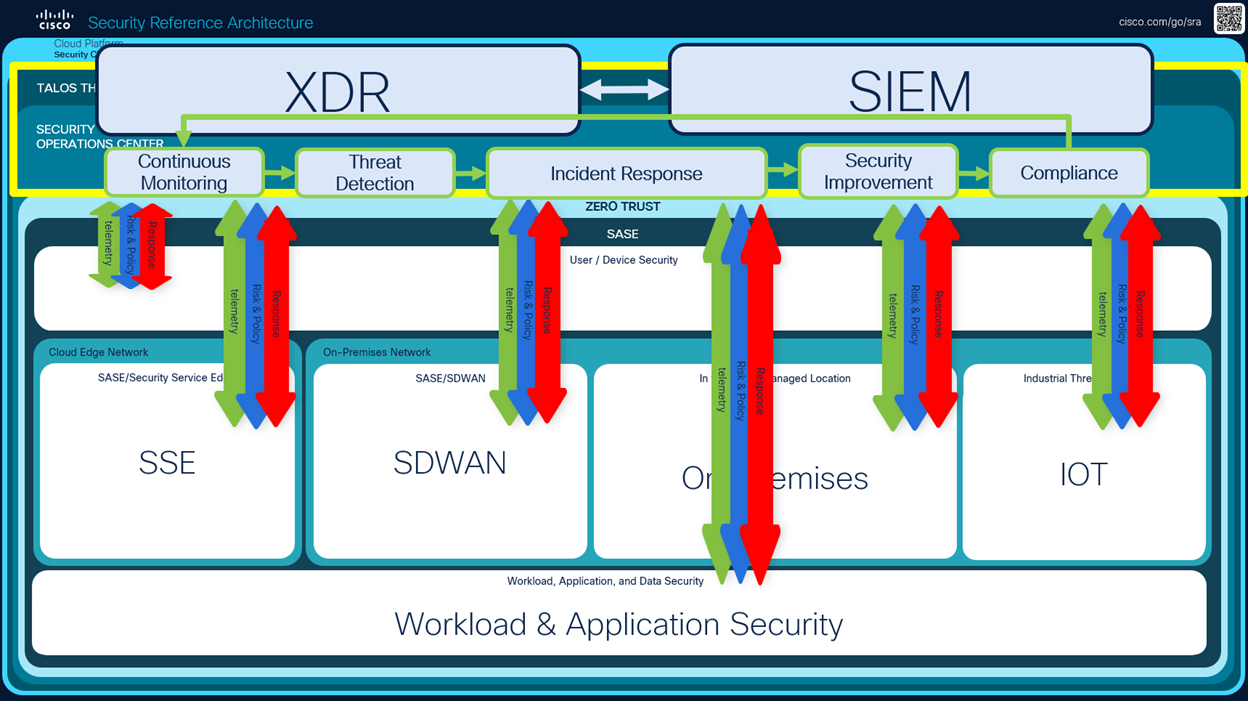
The Cisco Security Reference Architecture (SRA) provides an overview of the Cisco Security portfolio, commonly deployed use cases, and the recommended capabilities within an integrated architecture. The reference architecture maps to domains that align closely with industry security frameworks such as NIST, CISA, and DISA. The five main components of the reference architecture are listed below.
- Security cloud platform
- Security operations center
- User/device security
- Cloud edge and on-premises networks
- Workload and application security
Every organization has a unique environment based on business requirements. Not every listed capability is required to complete the architecture. We encourage you to connect with your Cisco account team and map out your security journey with us.